
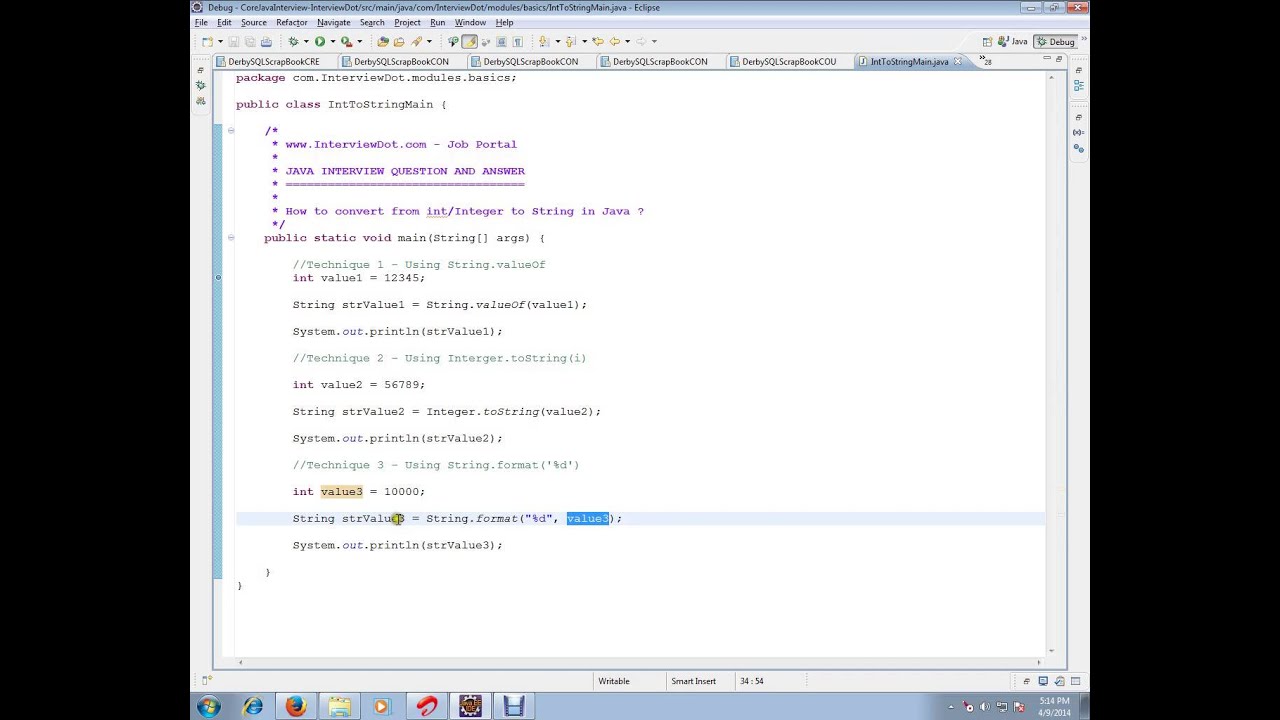
The object then iterates over each token and reads each token using its different methods. In this case, the scanner object will read the entire line and divides the string into tokens: " He", " is" and " 22".
#Java to swift converter online code#
Swift AST Explorer AST visualizer for Swift source code Visualize Swift AST and select nodes within the editor, a great way to learn about the structure of Swift syntax trees. Suppose there is an input string: He is 22 SwiftFiddle is an online playground for creating, sharing and embedding Swift fiddles (little Swift programs that run directly in your browser). Tokens are small elements that have some meaning to the Java compiler. The Scanner class reads an entire line and divides the line into tokens. In the above example, we have used the and package to read BigInteger and BigDecimal respectively. ("Enter a big decimal: ") īigDecimal value2 = input.nextBigDecimal() ("Enter a big integer: ") īigInteger value1 = input.nextBigInteger() nextBigDecimal() - reads the big decimal value from the userĮxample 4: Read BigInteger and BigDecimal import.nextBigInteger() - reads the big integer value from the user.Java scanner can also be used to read the big integer and big decimal numbers. Java Scanner with BigInteger and BigDecimal Recommended Reading: Java Scanner skipping the nextLine(). The method is terminated when it encounters a next line character, \n. Unlike next(), the nextLine() method reads the entire line of input including spaces. In the first example, we have used the nextLine() method to read a string from the user. Once the whitespace is encountered, it returns the string (excluding the whitespace).Įxample 5: Java Scanner nextLine() import This is because the next() method reads input up to the whitespace character. However, the next() method only reads the first name.

In the above example, we have used the next() method to read a string from the user. In the above example, we have used the nextDouble() method to read a floating-point value.Įxample 4: Java Scanner next() import In the above example, we have used the nextInt() method to read an integer value.Įxample 3: Java Scanner nextDouble() import The Scanner class provides various methods that allow us to read inputs of different types.Įxample 2: Java Scanner nextInt() import Here, we have created objects of the Scanner class that will read input from InputStream, File, and String respectively. Scanner sc1 = new Scanner(InputStream input) Once we import the package, here is how we can create Scanner objects. To learn more about importing packages, visit Java Packages. Now that you have some idea about Scanner, let's explore more about it.Īs we can see from the above example, we need to import the package before we can use the Scanner class. We have then used the nextLine() method of the Scanner class to read a line of text from the user. It works just like taking inputs from the keyboard. The System.in parameter is used to take input from the standard input. Here, we have created an object of Scanner named input. In the above example, notice the line Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in) Let's take an example.Įxample 1: Read a Line of Text Using Scanner import Java is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.The Scanner class of the java.util package is used to read input data from different sources like input streams, users, files, etc. For details, see the Google Developers Site Policies. RequirementsĮxcept as otherwise noted, the content of this page is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License, and code samples are licensed under the Apache 2.0 License.
#Java to swift converter online android#
Developers must have sourceĬode for their Android app, which they either own or are licensed to use. J2ObjC cannot convert Android binary applications. UIs using Android's API, web app UIs using GWT, etc.). We believe that iOS UI code needs toīe written in Objective-C, Objective-C++ or Swift using Apple's iOS SDK (Android J2ObjC does not provide any sort of platform-independent UI toolkit, nor are Translation and execution is also supported. J2ObjC supports most Java language and runtime features required byĬlient-side application developers, including exceptions, inner andĪnonymous classes, generic types, threads and reflection. Shared by web apps (using GWT), Android apps, The goal is to write an app's non-UIĬode (such as application logic and data models) in Java, which is then This toolĮnables Java source to be part of an iOS application's build, as no editing Java source code to Objective-C for the iOS (iPhone/iPad) platform. J2ObjC is an open-source command-line tool from Google that translates


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
